Checked by the Top One Trader editorial team, experienced traders and analysts are committed to providing reliable, practical insights for funded trading success.
Millions of people trade the forex market today, and many of them are Muslims who face the same recurring concern: Is forex trading halal or haram? The market offers real opportunities for traders, but not every trading practice aligns with Islamic principles.
Because of this, many Muslim traders feel confused or worried about whether participating in forex is religiously permissible.
This guide clears that confusion by explaining when forex becomes halal or haram and offering practical steps to help you trade in full alignment with Islamic guidelines.
Key Takeaways
- This article explains exactly when forex trading is considered halal or haram, using clear Islamic finance principles such as riba, gharar, and maisir, so Muslim traders can understand what is religiously permissible.
- You will learn how to trade forex in a fully halal way, including the conditions required, practical steps to stay compliant, and how to avoid trading practices that violate Islamic guidelines.
What Makes Forex Trading Halal or Haram? (Core Islamic Principles)
Understanding whether forex trading is halal or haram begins with the foundations of Islamic finance and sharia law. Islamic financial systems are built on fairness, transparency, and ethical conduct, ensuring that all transactions support legitimate value and avoid exploitation.
Three major prohibitions guide Islamic rulings on finance and trading:
1. Riba (Interest)
Riba refers to any guaranteed or automatic interest, and it is strictly forbidden.
In forex, this usually appears through:
- Overnight swap charges
- Interest-based rollover fees
- Earning or paying interest on leveraged positions
Most conventional forex accounts apply swaps when positions stay open overnight, making them non-compliant unless replaced with a swap-free Islamic account.
2. Gharar (Excessive Uncertainty)
Gharar occurs when a transaction involves ambiguity, unclear terms, or unknown outcomes.
In forex, gharar may appear in:
- Contracts without clear ownership
- Instruments with uncertain settlement timing
- Financial products based on unclear or unverifiable terms
High-risk speculative behaviour or unclear delivery also falls into this category.
3. Maisir (Gambling / Pure Speculation)
Maisir refers to activities where the outcome depends largely on chance instead of skill or analysis.
In forex, this includes:
- Extremely high-leverage trading
- Random, impulsive trading with no analysis
- Binary options and similar speculative products that function like price wagers rather than real trading
Islamic scholars consider such behaviour impermissible because it resembles gambling.
Ready to put your trading knowledge into practice?
Trade with Top One Trader and access a trusted funding programme built for serious traders. Get transparent rules, fast payouts, and a supportive trading environment as you work towards consistency.
Is Forex Trading Halal?
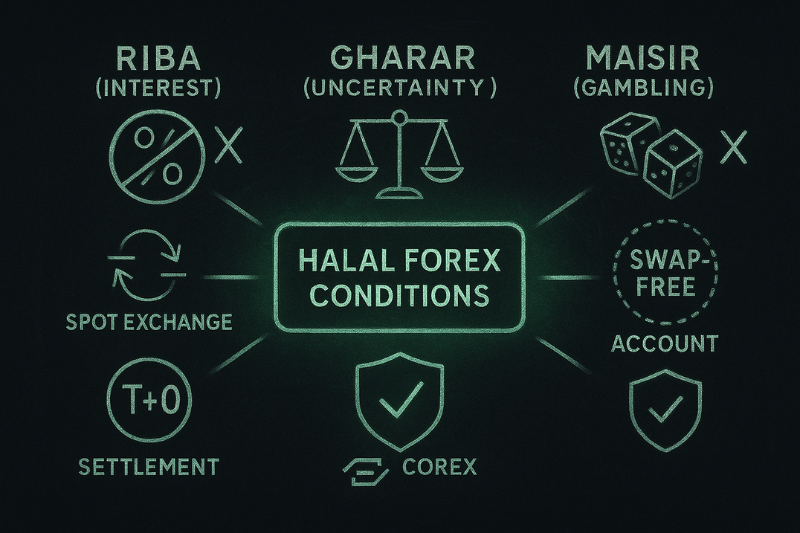
Forex trading can be halal — but only when it meets specific Islamic requirements. When FX trading follows Sharia conditions such as immediate exchange, fairness, and the absence of interest, it becomes a permissible form of currency exchange rather than speculation. When FX trading meets Islamic requirements, it aligns with the principles of ṣarf (currency exchange) recognised in Islamic jurisprudence, allowing Muslim traders to participate without compromising their beliefs.
To be considered halal, a forex transaction must follow Islamic criteria:
1. Spot trading with immediate exchange (T+0)
Forex becomes halal when currencies are exchanged instantly at the moment of trade. This fulfils the Islamic “hand-to-hand” requirement for ṣarf, ensuring no delay or uncertainty. Immediate settlement keeps the transaction transparent and compliant.
2. No interest of any kind (no swap fees)
Islam strictly prohibits riba, meaning no trader can pay or receive interest. Swap-free Islamic accounts remove overnight fees so positions can be held without violating this rule. This ensures the transaction remains clean and fully sharia-compliant.
3. Transparent, fair contracts
All terms, pricing, spreads, and execution must be clear before the trade is opened. Hidden conditions create gharar, an unacceptable form of uncertainty in Islamic finance. Transparency ensures fairness and protects both sides of the transaction.
4. Underlying economic value
Trades should reflect real currency exposure rather than products with no actual ownership. Many brokers offer forex through CFDs, which are price-based contracts rather than true currency exchange. Because CFDs do not involve delivery or ownership, their permissibility must be assessed carefully under Islamic guidelines.
5. Responsible use of leverage
Leverage itself is not automatically haram; it becomes problematic only when:
- The broker charges interest on borrowed funds
- The leverage level creates Maisir-like, high-risk behaviour
- Losses can exceed reasonable limits
In Islamic accounts, leverage is generally structured without interest, allowing it to be used within disciplined, risk-managed boundaries.
6. Trading with analysis and structure, not gambling
Halal trading relies on skill, research, and a reliable trading strategy, not chance. Impulsive decisions or random entries constitute maisir and violate Islamic rules. A structured, analytical approach keeps trading ethical and compliant.
7. Using a verified Islamic trading account
A legitimate Islamic account removes swaps completely and avoids disguised interest charges. Its fee structure must be transparent and fully disclosed to the trader. This provides a safe foundation for participating in halal forex.
How Islamic Scholars View Forex Trading
Islamic finance scholars generally agree that forex trading becomes permissible when these conditions are met, particularly the prohibition of riba, immediate settlement, avoidance of excessive uncertainty, and the presence of real economic value. Some scholarly interpretations differ slightly, depending on how modern instruments are assessed.
When these requirements are met, forex trading aligns with recognised Islamic jurisprudence on currency exchange, enabling Muslim traders to participate with confidence and in accordance with their faith.
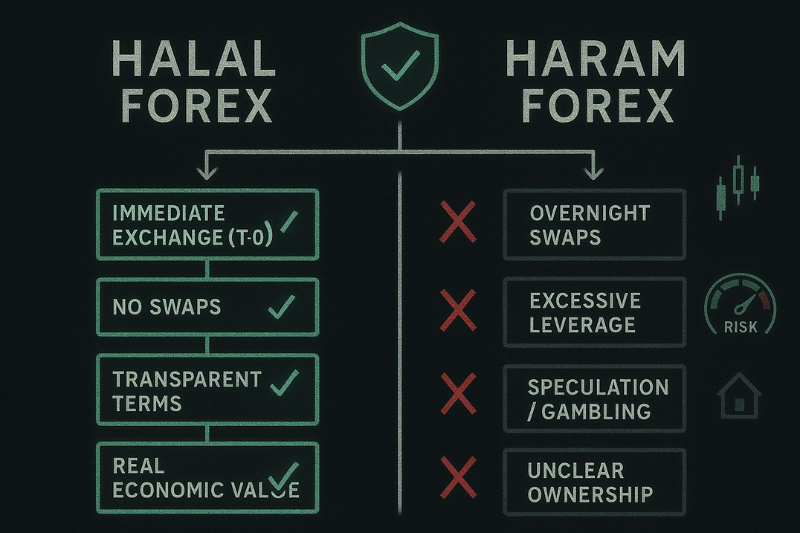
Is Forex Trading Haram?

Forex can be halal when structured correctly, but it becomes haram when FX violates Islamic principles through elements such as interest, excessive uncertainty, and speculation. The most common issue is the presence of overnight interest payments (swap fees). When a position is held past midnight, the trader earns or pays interest, creating a form of riba that is strictly prohibited in Islam.
Speculative Trading and Maisir
Forex may also become haram when trading resembles gambling rather than informed analysis. Impulsive entries, extreme risk-taking, or decisions driven by chance rather than strategy can fall under the category of maisir. Islam prohibits trading behaviour that is based on randomness rather than skill and structured planning.
Excessive Leverage Concerns
Another source of concern is the use of excessive leverage. In many traditional trading accounts, leverage involves borrowing funds from the broker, with or without explicit or implicit interest obligations. Even when interest is not directly charged, very high leverage introduces instability and excessive risk that contradict Islamic financial ethics.
Instruments with Unclear Ownership (CFDs)
Some financial instruments raise questions due to unclear ownership or settlement. CFDs and similar non-delivery contracts allow traders to speculate on price movements without owning the underlying currency. Because they lack actual delivery and may contain uncertainty in their structure, they are sometimes classified as gharar by Islamic scholars.
Situations Where Forex Is Considered Haram
Forex trading is generally regarded as haram when it includes:
- Holding positions that incur overnight interest
- Using leverage tied to interest-based borrowing
- Speculating with no economic purpose
- Trading contracts without clear ownership or delivery
Why This Matters for Muslim Traders
Understanding these prohibited elements helps Muslim traders recognise trading environments that may compromise Islamic values. By avoiding structures that include riba, gharar, or maisir, traders can maintain compliance with Islamic financial principles.
How to Trade Forex the Halal Way (Practical Guidance + Checklist)
Trading forex in a halal manner requires more than avoiding swaps; it means ensuring your entire trading environment aligns with Islamic principles. Muslim traders should avoid riba, minimise gharar, and avoid practices that resemble maisir. These guidelines matter because forex is part of the broader financial markets, where many financial transactions may unintentionally conflict with Islamic law. A structured approach helps traders remain compliant while maintaining professional discipline.
1. Choose a Broker or Prop Firm Offering Verified Islamic Accounts
Select a regulated broker or a prop firm that provides transparent, interest-free Islamic trading account options. A compliant account must eliminate swaps, offer clear pricing, and avoid speculative incentives such as risky bonuses.
2. Open a Proper Swap-Free Account
Confirm that the account removes overnight interest without replacing it with disguised fees. Some accounts marketed as “Islamic” reintroduce hidden charges or limit swap-free status to a few days, which is not acceptable.
3. Trade Using Halal Strategies
Spot trading, day trading, and swing trading can all be halal when based on genuine analysis, structured planning, and responsible risk management. Avoid random speculation or high-risk decisions.
4. Apply Islamic Rules on Leverage and Settlement
Use leverage cautiously, only when no interest is involved. All currency exchanges should follow the T+0 (hand-to-hand) settlement principle to avoid gharar.
Quick Guide: What a True Islamic Account Should Look Like
| Requirement | Halal Islamic Account | Non-Compliant Account |
| Interest (Riba) | No swaps, no interest | Hidden fees acting like interest |
| Settlement (Ṣarf) | Immediate exchange (T+0) | Unclear or delayed settlement |
| Fee Transparency | Clear, fixed, disclosed | Variable or unclear charges |
| Speculation Incentives | None | Bonuses encouraging risky trading |
| Sharia Oversight | Sometimes scholar-reviewed | No religious verification |
Halal Trading Checklist
- No interest-based charges
- Clear contract terms with no hidden fees
- Real economic exposure, not purely synthetic speculation
- Swap-free structure confirmed in writing
- Disciplined, analysis-based trading behaviour
By following these guidelines, Muslim traders can participate confidently in the financial markets while staying fully aligned with Islamic ethical principles and maintaining a trading style grounded in discipline and clarity under Islamic law.
Final Thoughts
Forex trading can be practised in a fully halal way, but long-term success depends on more than avoiding interest or meeting Islamic conditions. Consistent profitability comes from disciplined execution, strong risk management, and a well-defined strategy with a real trading edge, not speculation or chance.
When traders focus on thoughtful analysis, responsible position sizing, and continuous improvement, they build habits that honour both Islamic principles and professional trading standards. By combining ethical compliance with a structured, skill-based approach, Muslim traders can pursue financial growth while staying true to their values.
Take the next step in your trading journey!Join Top One Trader and access flexible accounts, transparent rules, fast payouts, and educational content designed to support your growth. With everything you need in one place, you can focus on improving your trading and building long-term consistency.


